Discover the Uses and Benefits of Beet Sugar Vs Cane Sugar in Your Daily Diet Plan
Checking out the unique qualities of beet and cane sugar exposes more than simply their sweetening capabilities; it highlights their special influence on health and cooking arts. Beet sugar, recognized for its subtle taste, is typically favored in delicate treats, whereas cane sugar, with its hint of molasses, includes richness to durable recipes. Each kind holds its very own nutritional profile and glycemic ramifications, welcoming a much deeper understanding of their functions in a well balanced diet regimen and lasting intake practices.
Origin and Production Processes of Beet and Cane Sugar
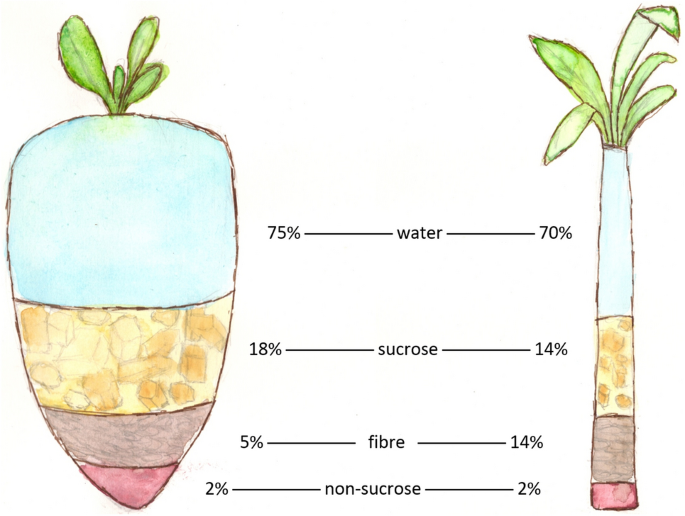
The unique environments and dirt types required for growing sugar beetroots and sugarcane add to distinctions in their growing techniques and geographic distribution, influencing the economics and sustainability of their manufacturing. beet sugar vs cane sugar.
Nutritional Contrast In Between Beet Sugar and Cane Sugar
Regardless of originating from different plants, beet sugar and cane sugar are nutritionally extremely similar, both primarily including sucrose. Each provides regarding 4 calories per gram, converting to roughly 16 calories per tsp. Structurally, both sugars are made up of about 99.95% sucrose, with minimal amounts of other substances like dampness and trace element, which do not significantly modify their dietary accounts.

Eventually, when choosing in between beet sugar and cane sugar based on nutritional web content alone, both deal identical benefits and drawbacks as they are essentially forms of the exact same particle-- sucrose, giving fast energy without various other nutrients.
Effect On Health: Glycemic Index and Caloric Content
Checking out additionally into the results of beet sugar and cane sugar on health, next it is essential to consider their glycemic index and calorie web content. Both sugars are identified as sucrose, which consists of sugar and fructose. This make-up leads them to have a similar effect on blood sugar levels. The glycemic index (GI) of both beet and cane sugar is around 65, categorizing them as high-GI foods, which can trigger fast spikes in blood sugar degrees. This is a crucial element for individuals managing diabetes or those trying to maintain their energy degrees throughout the day.
Each kind of sugar consists of about 4 calories per gram, making their caloric content matching. For those monitoring caloric consumption, particularly when handling weight or metabolic health problems, recognizing this equivalence is important (beet sugar vs cane sugar). Extreme consumption of any type of high-calorie, high-GI food can add to health and wellness concerns such as obesity, heart illness, and insulin resistance.
Environmental and Economic Factors To Consider of Sugar Production
Beyond health and wellness impacts, the manufacturing of beet and cane sugar additionally raises significant ecological and economic problems. Sugar beet cultivation often tends to need cooler climates and has a reduced geographical impact compared to sugar cane, which grows in exotic areas.
Additionally, using chemicals and fertilizers in both beet and cane sugar farming look here can lead to dirt degradation and air pollution, more influencing biodiversity and neighborhood water bodies (beet sugar vs cane sugar). The choice in between growing sugar beet or cane frequently depends upon regional ecological conditions and economic aspects, making the sustainability of sugar manufacturing a my link complicated issue
Culinary Applications and Flavor Distinctions
While the ecological and economic facets of sugar production are indeed substantial, the option in between beet and cane sugar likewise influences cooking applications and flavor accounts. Beet sugar, stemmed from the sugar beet plant, is recognized for its remarkably neutral taste. This makes it a versatile component in cooking, where it does not modify the flavor of various other components. It dissolves promptly and is ideal for usage in cakes, cookies, and breads.
Cane sugar, removed from sugarcane, usually retains molasses traces, which give a distinct richness and deepness. This slight molasses taste boosts the complexity of baked products, sauces, and sauces. It is specifically preferred in items where a sugar touch is preferred, such as in brownies or gingerbread. The slight variation in wetness content in between beet and cane sugar can affect the appearance and uniformity of dishes, making cane sugar a preferred choice for certain recipes that benefit from its one-of-a-kind residential properties.

Conclusion
To conclude, both beet and cane sugar have distinct beginnings and production processes, providing similar nutritional accounts with slight distinctions in sodium web content and taste. While their effect on wellness, specifically pertaining to glycemic index and calories, is equivalent, the option in between them often comes down to environmental, economic elements, and certain culinary needs. Recognizing these facets can direct consumers in making notified decisions that line up with their wellness goals and taste preferences.